Under the Blue Box Regulation, consumers are individuals who use a product and its packaging for personal, family or household purposes, or persons who use a beverage and its container for personal, family, household, or business purposes.
Topic: Producer
Are Blue Box materials that are supplied to the IC&I sector, such as long-term care homes, obligated?
Blue Box materials supplied to a business (e.g., the operators of a long-term care home) are not obligated, however, there are no deductions available for materials supplied to a consumer in an IC&I setting (e.g., a resident of a long-term care home).
Any Blue Box materials supplied to consumers in Ontario are obligated. Blue Box materials supplied to the IC&I sector are not obligated (except beverage containers which are obligated regardless of the sector supplied into).
If a marketplace facilitator supplies products for which there is a brand holder resident in Canada, who is the obligated producer?
The brand holder is the obligated producer.
A marketplace facilitator only becomes obligated for products supplied through its marketplace where the producer would have been a retailer. If the producer is a brand holder or an importer, they remain the obligated producer even when products are distributed by a marketplace facilitator.
A retailer is a business that supplies products to consumers, whether online or at a physical location.
Are containers that are obligated under the Hazardous and Special Products (HSP) Regulation obligated as Blue Box materials?
No, products or packaging designated as Hazardous and Special Products (HSP) are not obligated under the Blue Box Regulation. For example, primary packaging for paints and coatings are HSP and therefore not obligated as Blue Box materials.
Some packaging for HSP products may still be obligated. For example, the packaging that contains an oil filter is obligated as Blue Box materials.
Consult the HSP Regulation or the Compliance and Registry Team for further information.
Is transport packaging that is removed by a retail location and not supplied to the consumer obligated?
No, transport packaging is only obligated when supplied to a consumer in Ontario. Any transport packaging removed by a retailer or other entity before the product is supplied to a consumer is not obligated under this regulation.
Am I a producer of paper products or packaging-like products?
See our FAQs to understand “What are paper products?” and “What are packaging-like products?”.
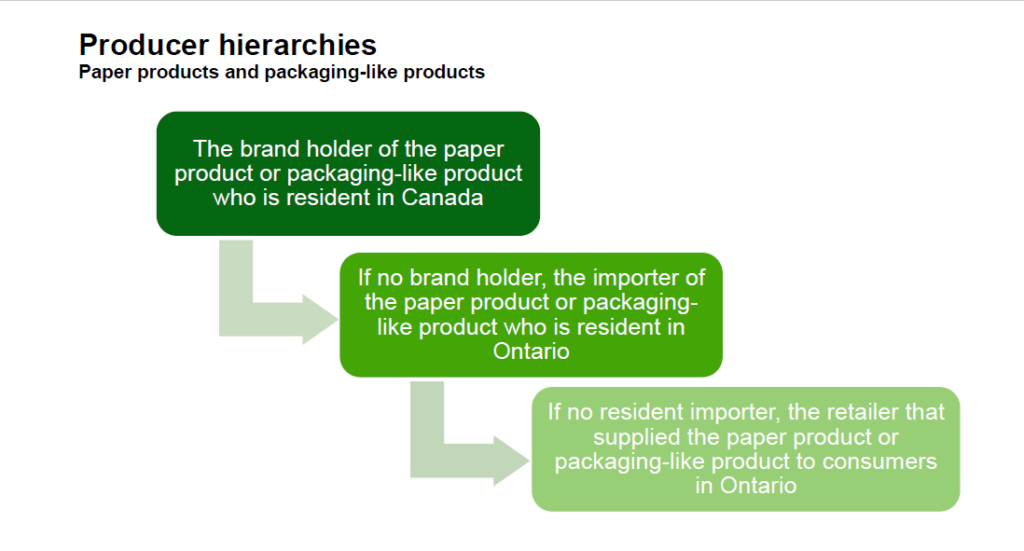
For paper products and packaging-like products, a person is considered a producer:
- if they are the brand holder of the paper product or packaging-like product and are resident in Canada
- if no resident brand holder, they are resident in Ontario and import the paper product or packaging-like product from outside of Ontario
- if no resident importer, they are the retailer that supplied the paper product or packaging-like product directly to consumers in Ontario
- if the retailer who would be the producer is a marketplace seller, the marketplace facilitator is the obligated producer
- if the producer is a business that is a franchise, the franchisor is the obligated producer, if that franchisor has franchisees that are resident in Ontario
Am I a producer of Blue Box product packaging?
See our FAQ to understand “What is blue box product packaging?”.
Product packaging added to a product can be added at any stage of the production, distribution and supply of the product. A person adds packaging to a product if they:
- make the packaging available for another person to add the packaging to the product
- cause another person to add the packaging to a product
- combine the product and the packaging
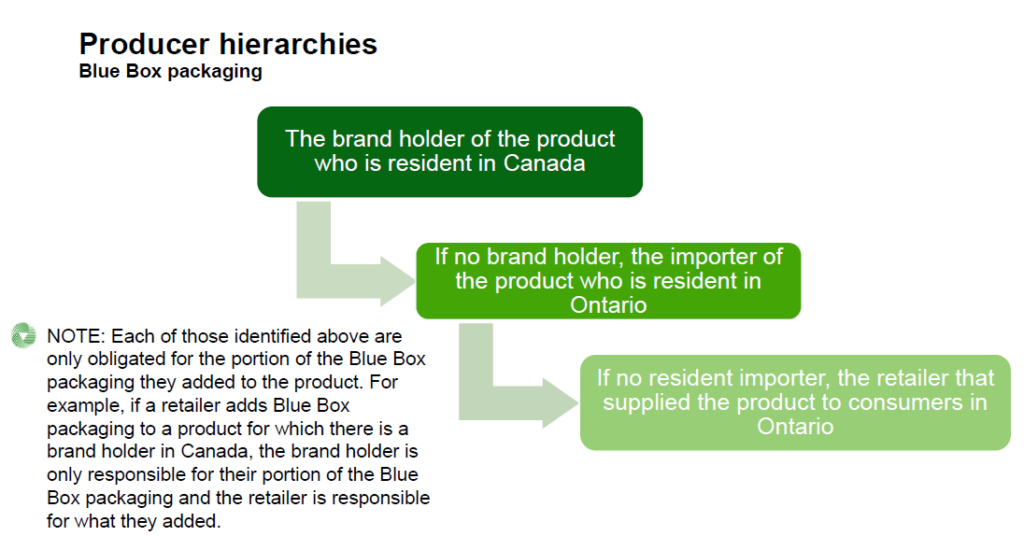
For the portion of the product packaging that a brand holder added to the product, a person is considered a producer:
- if they are the brand holder of the product and are resident in Canada
- if no resident brand holder, they are resident in Ontario and import the product from outside of Ontario
- if no resident importer, they are the retailer that supplied the product directly to consumers in Ontario
- if the retailer who would be the producer is a marketplace seller, the marketplace facilitator is the obligated producer
- if the producer is a business that is a franchise, the franchisor is the obligated producer, if that franchisor has franchisees that are resident in Ontario
For the portion of the product packaging that an importer of the product into Ontario added to the product, a person is considered a producer:
- if they are resident in Ontario and import the product from outside of Ontario
- if no resident importer, they are the retailer that supplied the product directly to consumers in Ontario
- if the retailer who would be the producer is a marketplace seller, the marketplace facilitator is the obligated producer
- if the producer is a business that is a franchise, the franchisor is the obligated producer, if that franchisor has franchisees that are resident in Ontario
For any portion of the packaging that is not described above, the producer is the retailer who supplied the product to consumers in Ontario.
Why is a registration and/or reporting deadline communicated by the Authority different than what is written in the regulation?
What is blue box product packaging?
Under the Blue Box Regulation, blue box product packaging includes:
- Primary packaging is for the containment, protection, handling, delivery and presentation of a product at the point of sale, including all packaging components, but does not include convenience packaging or transport packaging (e.g., film and cardboard used to package a 24-pack of water bottles and the label on the water bottle).
- Transportation packaging which is provided in addition to primary packaging to facilitate the handling or transportation of one or more products such as a pallet, bale wrap or box, but does not include a shipping container designed for transporting things by road, ship, rail or air.
- Convenience packaging includes service packaging and is used in addition to primary packaging to facilitate end users’ handling or transportation of one or more products. It also includes packaging that is supplied at the point of sale by food-service or other service providers to facilitate the delivery of goods and includes items such as bags and boxes that are supplied to end users at check out, whether or not there is a separate fee for these items.
- Service accessories are products supplied with a food or beverage product and facilitate the consumption of that food or beverage product and are ordinarily disposed of after a single use, whether or not they could be reused (e.g., a straw, cutlery or plate).
- Ancillary elements are integrated into packaging (directly hung or attached to packaging) and are intended to be consumed or disposed of with the primary packaging. Ancillary elements help the consumer use the product. Examples of ancillary packaging include a mascara brush forming part of a container closure, a toy on the top of candy acting as part of the closure, devices for measuring dosage that form part of a detergent container cap, or the pouring spout on a juice or milk carton.
What are paper products?
Under the Blue Box Regulation, paper products include printed and unprinted paper, such as a newspaper, magazine, greeting cards, calendars (promotional or purchased), notebooks and daily planners, promotional material, directory, catalogue or paper used for copying, writing or any other general use.
Hard or soft cover books and hardcover periodicals are not considered paper products.
What are packaging-like products?
Under the Blue Box Regulation, a packaging-like product is:
- ordinarily used for the containment, protection, handling, delivery, presentation or transportation of things
- ordinarily disposed of after a single use
- not used as packaging when it is supplied to the consumer
Packaging-like products include aluminum foil, a metal tray, plastic film, plastic wrap, wrapping paper, a paper bag, beverage cup, plastic bag, cardboard box or envelope, but does not include a product made from flexible plastic that is ordinarily used for the containment, protection, or handling of food, such as cling wrap, sandwich bags, or freezer bags.
If a producer is unsure whether or not their product is a packaging-like product, they can ask themselves the following questions to help determine whether the product is obligated to be reported under the Blue Box Regulation:
- Is the product actually packaging around a separate product?
- If yes, the product is not a packaging-like product. Instead, the product is considered blue box packaging and must be reported as blue box material. If no, continue to the next question.
- Is the product used for the containment, protection, handling, delivery, presentation or transportation of a thing(s)?
- If no, the product is not a packaging-like product. If yes, continue to the next question.
- Is the product typically disposed of after a single use (regardless if some may wash and reuse it)?
- If no, the product is not a packaging-like product. If yes, continue to the next question.
- Is the product made from flexible plastic that is for the containment, protection or handling of food?
- If yes, the product is not a packaging-like product. If no, the product is a packaging-like product and must be reported as blue box material.
If a producer is still unsure whether or not their product is a packaging-like product, they should contact the Compliance and Registry Team at 833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
Can I dispute an environmental fee that seems too high?
If you are concerned about the fee you were charged, you should contact the business that charged you the fee to request a more detailed explanation of how the fee was determined.
Is the environmental fee on my receipt a tax?
No. An environmental fee is not a government tax and cannot be represented as mandatory, a regulatory charge, or a RPRA fee. It is a fee charged at the discretion of a business to recover their costs related to recycling the product.