
Frequently Asked Questions
Results (26)
Click the question to read the answer.
-
Under the Blue Box Regulation, blue box product packaging includes:
- Primary packaging is for the containment, protection, handling, delivery and presentation of a product at the point of sale, including all packaging components, but does not include convenience packaging or transport packaging (e.g., film and cardboard used to package a 24-pack of water bottles and the label on the water bottle).
- Transportation packaging which is provided in addition to primary packaging to facilitate the handling or transportation of one or more products such as a pallet, bale wrap or box, but does not include a shipping container designed for transporting things by road, ship, rail or air.
- Convenience packaging includes service packaging and is used in addition to primary packaging to facilitate end users’ handling or transportation of one or more products. It also includes packaging that is supplied at the point of sale by food-service or other service providers to facilitate the delivery of goods and includes items such as bags and boxes that are supplied to end users at check out, whether or not there is a separate fee for these items.
- Service accessories are products supplied with a food or beverage product and facilitate the consumption of that food or beverage product and are ordinarily disposed of after a single use, whether or not they could be reused (e.g., a straw, cutlery or plate).
- Ancillary elements are integrated into packaging (directly hung or attached to packaging) and are intended to be consumed or disposed of with the primary packaging. Ancillary elements help the consumer use the product. Examples of ancillary packaging include a mascara brush forming part of a container closure, a toy on the top of candy acting as part of the closure, devices for measuring dosage that form part of a detergent container cap, or the pouring spout on a juice or milk carton.
-
Under the Blue Box Regulation, a packaging-like product is:
- ordinarily used for the containment, protection, handling, delivery, presentation or transportation of things
- ordinarily disposed of after a single use
- not used as packaging when it is supplied to the consumer
Packaging-like products include aluminum foil, a metal tray, plastic film, plastic wrap, wrapping paper, a paper bag, beverage cup, plastic bag, cardboard box or envelope, but does not include a product made from flexible plastic that is ordinarily used for the containment, protection, or handling of food, such as cling wrap, sandwich bags, or freezer bags.
If a producer is unsure whether or not their product is a packaging-like product, they can ask themselves the following questions to help determine whether the product is obligated to be reported under the Blue Box Regulation:
- Is the product actually packaging around a separate product?
- If yes, the product is not a packaging-like product. Instead, the product is considered blue box packaging and must be reported as blue box material. If no, continue to the next question.
- Is the product used for the containment, protection, handling, delivery, presentation or transportation of a thing(s)?
- If no, the product is not a packaging-like product. If yes, continue to the next question.
- Is the product typically disposed of after a single use (regardless if some may wash and reuse it)?
- If no, the product is not a packaging-like product. If yes, continue to the next question.
- Is the product made from flexible plastic that is for the containment, protection or handling of food?
- If yes, the product is not a packaging-like product. If no, the product is a packaging-like product and must be reported as blue box material.
If a producer is still unsure whether or not their product is a packaging-like product, they should contact the Compliance and Registry Team at 833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
-
See our FAQ to understand “What is blue box product packaging?”.
Product packaging added to a product can be added at any stage of the production, distribution and supply of the product. A person adds packaging to a product if they:
- make the packaging available for another person to add the packaging to the product
- cause another person to add the packaging to a product
- combine the product and the packaging
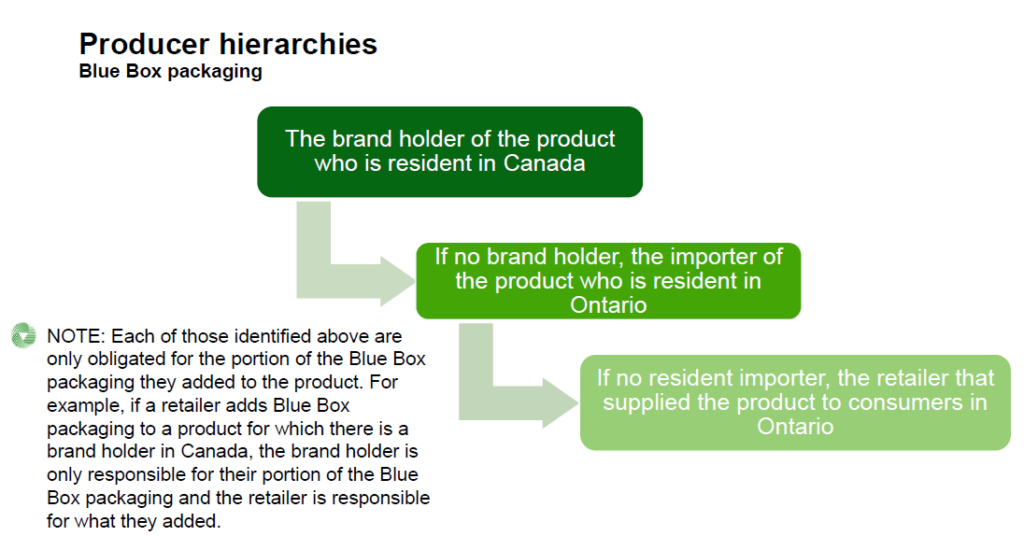
For the portion of the product packaging that a brand holder added to the product, a person is considered a producer:
- if they are the brand holder of the product and are resident in Canada
- if no resident brand holder, they are resident in Ontario and import the product from outside of Ontario
- if no resident importer, they are the retailer that supplied the product directly to consumers in Ontario
- if the retailer who would be the producer is a marketplace seller, the marketplace facilitator is the obligated producer
- if the producer is a business that is a franchise, the franchisor is the obligated producer, if that franchisor has franchisees that are resident in Ontario
For the portion of the product packaging that an importer of the product into Ontario added to the product, a person is considered a producer:
- if they are resident in Ontario and import the product from outside of Ontario
- if no resident importer, they are the retailer that supplied the product directly to consumers in Ontario
- if the retailer who would be the producer is a marketplace seller, the marketplace facilitator is the obligated producer
- if the producer is a business that is a franchise, the franchisor is the obligated producer, if that franchisor has franchisees that are resident in Ontario
For any portion of the packaging that is not described above, the producer is the retailer who supplied the product to consumers in Ontario.
-
See our FAQs to understand “What are paper products?” and “What are packaging-like products?”.
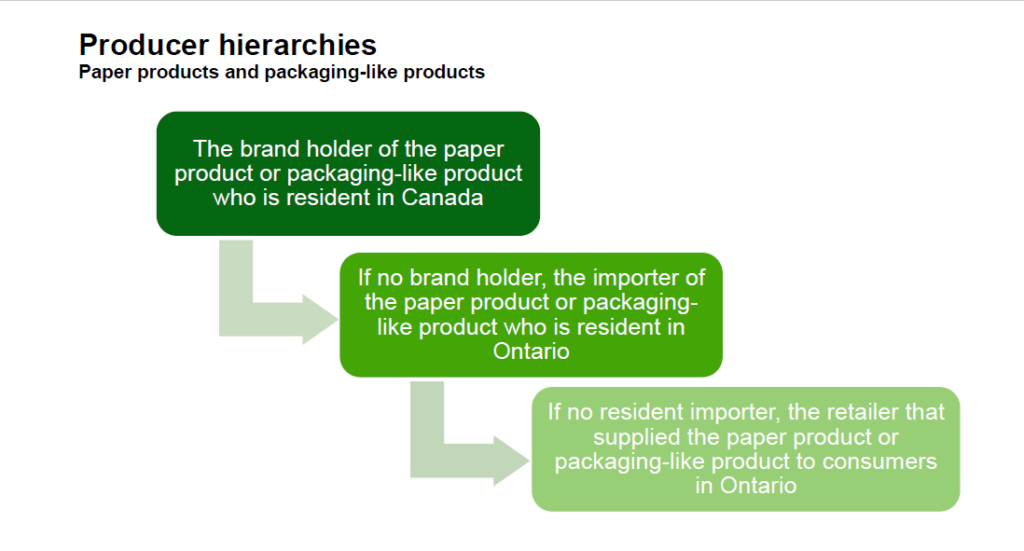
For paper products and packaging-like products, a person is considered a producer:
- if they are the brand holder of the paper product or packaging-like product and are resident in Canada
- if no resident brand holder, they are resident in Ontario and import the paper product or packaging-like product from outside of Ontario
- if no resident importer, they are the retailer that supplied the paper product or packaging-like product directly to consumers in Ontario
- if the retailer who would be the producer is a marketplace seller, the marketplace facilitator is the obligated producer
- if the producer is a business that is a franchise, the franchisor is the obligated producer, if that franchisor has franchisees that are resident in Ontario
-
In the Blue Box Regulation, certified compostable products and packaging is defined as material that:
- is only capable of being processed by composting, anaerobic digestion or other processes that result in decomposition by bacteria or other living organisms, and
- is certified compostable by an international, national, or industry standard that is listed in this procedure.
All certified compostable products and packaging reported by producers must be certified under one of the following standards:
- CAN/BNQ 0017-088: Specifications for Compostable Plastics
- ISO 17088: Specifications for compostable plastics
- ASTM D6400: Standard Specification for Labeling of Plastics Designed to be Aerobically Composted in Municipal or Industrial Facilities
- ASTM D6868: Standard Specification for Labeling of End Items that Incorporate Plastics and Polymers as Coatings or Additives with Paper and Other Substrates Designed to be Aerobically Composted in Municipal or Industrial Facilities
- EN 13432: Requirements for packaging recoverable through composting and biodegradation – Test scheme and evaluation criteria for the final acceptance of packaging
-
For the purposes of supply data reporting, ‘refillable packaging’ is defined as packaging surrounding a supplied product that a consumer can return to the product manufacturer for cleaning and reuse.
A producer who supplies its products in refillable packaging should only report weights (under the appropriate material category) the first time the packaging is supplied to consumers.
For example:
A milk producer that used 1000 new glass bottles to supply its product to consumers in 2022, reported the weight of all 1000 bottles under the beverage container category in their 2023 supply data report.
In 2023, the producer added 500 new glass bottles to its supply, bringing the total of supplied material to 1500 bottles. Their 2024 supply data report should only reflect the weights of the 500 new bottles, not the total currently being used by the producer (1500).
Important: Products supplied in beverage containers should be reported in the ‘beverage container’ category, not the category the container is made of (plastic, metal, glass).
See Compliance Bulletin: What blue box materials need to be reported?
-
Public sector institutions must report all branded and unbranded Blue Box packaging supplied or sold with food served in their owned and operated on-site facilities. These facilities include but are not limited to cafeterias, pubs, cafes, and in the case of a college or university, faculty offices.
It is important to consider other situations where food service Blue Box packaging is supplied to consumers. For example, a college must report the packaging used in their Culinary and Hospitality programs that allow students to take home food prepared in class.
-
No, transport packaging is only obligated when supplied to a consumer in Ontario. Any transport packaging removed by a retailer or other entity before the product is supplied to a consumer is not obligated under this regulation.
-
Unbranded products are products that do not have any mark, word, name, symbol, design, device or graphical element, or any combination of these, including a registered or unregistered trademark, which identifies a product and distinguishes it from other products.
The retailer who supplied the product to a consumer in Ontario, either online or at a physical location, is the obligated producer for the supply of Blue Box packaging on that unbranded product.
For example: A cucumber in plastic film sold at a grocery store that does not have any stickers, labeling or any other information associated with a brand is considered unbranded. As the retailer for that unbranded product, the grocery store is the obligated producer for the packaging supplied with the cucumber.
-
Each Blue Box producer is required to report the Blue Box packaging they add to a product.
For example: a college or university bookstore plans to ship a book to a consumer in Ontario. The bookstore staff packages the book in a small box with the packing slip and inserts the box into a plastic mailer supplied by the delivery service with the required label affixed.
In this scenario, the college or university is the obligated producer of the small box and packing slip and must report these materials in their supply report, whereas the delivery company is the obligated producer of the plastic mailer and label and must report these materials in their supply report.
-
Producers are not required to collect and manage their own branded products and materials. Instead, a producer is expected to collect and manage a portion of similar materials in Ontario. The portion of material that a producer collects and manages is known as their minimum management requirement. A minimum management requirement, which is set based on calculations outlined in the applicable Regulation, is the weight of the products or packaging that the producer must ensure is collected and managed. The calculated amount is proportionate to the weight of materials that producer supplied into the province.
For example, a producer who supplied laptops into Ontario does not need to collect and manage their own branded laptops. Instead, they must ensure that they collect and manage an equivalent weight of information technology, telecommunications, and audio-visual equipment (ITT/AV) materials.
Similarly, a producer who supplied cardboard boxes into Ontario does not need to collect and manage those exact cardboard boxes. Rather, they need to ensure that an equivalent weight of paper is collected and managed.
Almost all producers will work with producer responsibility organizations (PROs) for the purposes of meeting their obligations to collect and manage materials. PROs establish collection and management systems across Ontario for different material types. A producer can meet their obligations to collect and manage materials by entering into a contract with a PRO to provide these services on their behalf.
-
Blue Box materials (i.e., products and packaging made of metal, glass, paper, flexible plastic, rigid plastic, and beverage containers) are typically collected directly from residences through the provincial Blue Box Program. RPRA’s Where to Recycle map displays public locations for recycling materials that don’t belong in your Blue Box (e.g., batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste, lighting and tires).
For more information on recycling Blue Box materials, visit Circular Materials’ website. Circular Materials is the administrator of Ontario’s Blue Box collection system.
-
No, products or packaging designated as Hazardous and Special Products (HSP) are not obligated under the Blue Box Regulation. For example, primary packaging for paints and coatings are HSP and therefore not obligated as Blue Box materials.
Some packaging for HSP products may still be obligated. For example, the packaging that contains an oil filter is obligated as Blue Box materials.
Consult the HSP Regulation or the Compliance and Registry Team for further information.
-
Yes, reusable bags made from Blue Box materials ( e.g. plastic, paper) and used as convenience packaging are obligated under the Blue Box Regulation and must be reported annually by producers in their supply report.
Convenience packaging refers to material that is provided with a product for consumers to handle or transport that product, in addition to the product’s primary packaging. This includes items such as bags and boxes that are supplied to consumers at check out.
For additional clarity:
- Reusable bags made primarily from plastic, paper, or any other Blue Box material, or a combination of these materials, are obligated. Reusable bags made from textile fibres such as cotton, hemp, bamboo, etc., are not obligated.
- Recycled content of the material has no impact on whether a reusable bag is obligated. For example, reusable bags containing post-consumer recycled plastic content are obligated.
- A reusable bag is obligated regardless of whether it is supplied to the consumer for free or at a cost. Examples include bags supplied at checkout to consumers at retail locations.
If you haven’t been reporting reusable bags as part of your annual supply data, please contact the Compliance Team immediately at registry@rpra.ca.
Also see our FAQ: ‘What do I do if I misreported my supply data?’
-
The following are the types of Blue Box Materials obligated under the Blue Box Regulation:
- Blue box packaging (primary, transport, convenience, service accessories, ancillary elements)
- Paper products
- Packaging-like products
-
For the purposes of the Blue Box Regulation, a beverage container is a container that:
- Contains a ready-to-drink beverage product,
- “Ready-to-drink” means a beverage packaged by the manufacturer for immediate consumption that does not require any preparation. A ready-to-drink beverage is intended to be consumed as purchased and does not require a dispensing device to be consumed.
- “Beverage” means a consumable liquid for enjoyment or hydration. It does not include an “alcoholic beverage”, or “non-alcoholic beer, wine or spirits” as defined in O. Reg. 391/21.
- Is made from metal, glass, paper or rigid plastic, or any combination of these materials, and
- If a beverage container is made only of flexible plastic, it would be obligated as a Blue Box material but would be reported under the material category “Flexible Plastic” rather than the “Beverage Container” material category. The Blue Box Regulation defines flexible plastic as unmoulded plastic. For more information on reporting of packaging and beverage containers that consist of multiple materials, please see the “Component Threshold Rule” in the Blue Box Verification and Audit Procedure Registry Procedure.
- Is sealed by its manufacturer.
- A cup provided to a consumer in a restaurant filled with fountain pop is not sealed by the manufacturer and is therefore not considered a beverage container. However, the cup (including the lid and straw) would still be obligated as a Blue Box material in the paper and/or plastic material categories.
For greater clarity, the Registrar does not consider the packaging from the following product types to be a beverage container:
- Infant formula
- Meal replacements, nutritional supplements or dietary supplements
- Regulated health products
- Concentrated beverages intended to be mixed or diluted before consumption, such as frozen juices, cocktail mixers, extracts and flavour enhancers
- Liquids that are not intended to be consumed as purchased such as soup, syrups, cream and other beverage additives, whipping cream, buttermilk, broth
- Beverage containers made of flexible plastics such as milk bags (these are still to be reported as flexible plastics)
Milk products and substitutes (e.g., soy beverage, almond beverage, a rigid plastic container of milk, drinkable yogurt) are beverage containers provided they are packaged in a container as defined above.
- Contains a ready-to-drink beverage product,
-
Paints, pesticides, solvents fertilizers obligated under the HSP Regulation along with their primary packaging must be accepted at collection sites collecting the corresponding material. For instance, empty paint cans and pesticide aerosols obligated under the HSP Regulation must be accepted at collection sites collecting paint and pesticides.
See our FAQ to understand “Under the HSP Regulation, is the packaging of antifreeze, pesticides, solvents, paints and coatings obligated?” and “Are containers that are obligated under the HSP Regulation obligated as Blue Box materials?“
-
A producer’s management requirement is how much Blue Box material they must ensure is collected and processed into recovered resources each year. Management requirements are calculated based on what they supplied into Ontario one year prior and the resource recovery percentage as set in the regulation. A producer’s management requirement is calculated separately for each Blue Box material category (beverage container, glass, flexible plastic, rigid plastic, metal and paper).
Some producer are exempt from having a management requirement based on their supply data, for more information on exemptions see the FAQ Are there exemptions for Blue Box producers? A producer that does not have a management requirement does not have any collection, management or promotion and education obligations.
A producer with a management requirement must also provide collection and promotion and education services in Ontario. Most producers will contract the services of a producer responsibility organization (PRO) to meet their collection, management and promotion and education obligations.
To view your management requirement(s), log into your registry account, download a copy of your Blue Box Supply Report and review the section with your minimum management requirements. Management requirement for a given year are determine by supply data from two years prior. For example, 2023 management requirements were based on 2021 supply data (submitted in producers’ 2022 Supply Report).
Unsure if you are a Blue Box producer? See our FAQs Am I a producer of Blue Box product packaging? And Am I a producer of paper products and packaging-like products?
-
Brand holders and producers that supply products and packaging are required by legislation to meet individual mandatory collection and resource recovery requirements and may face compliance and enforcement consequences for failing to do so. The executive attestation ensures that executives responsible for managing the brand holder’s or producer’s business are aware of these requirements and can ensure that appropriate measures are put in place to achieve compliance with the regulations.
-
Individual Producer Responsibility (IPR) means that producers are responsible and accountable for collecting and managing their products and packaging after consumers have finished using them.
For programs under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 (RRCEA), producers are directly responsible and accountable for meeting mandatory collection and recycling requirements for end of life products. With IPR, producers have choice in how they meet their requirements. They can collect and recycle the products themselves, or contract with producer responsibility organizations (PROs) to help them meet their requirements.
-
Under the Blue Box Regulation, consumers are individuals who use a product and its packaging for personal, family or household purposes, or persons who use a beverage and its container for personal, family, household, or business purposes.
-
Producers are required to provide the following information when registering with RPRA:
- Contact information
- PRO information (if a PRO has been retained at time of reporting), including what services they have retained a PRO for
- Their 2020 supply data in each of the seven material categories– beverage container, glass material, flexible plastic, metal material, paper material, and certified compostable products and packaging material – as well as any deductions.
Please note that this information must be submitted to RPRA directly.
See our FAQ to understand “What deductions are available to producers under the Blue Box Regulation?”
-
Starting in 2022, producers are required to report their supply data annually to RPRA.
Each year, producers will need to provide the previous years’ supply data in each of the seven material categories – beverage container, glass material, flexible plastic, rigid plastic, metal material, paper material, and certified compostable products and packaging material – as well as any deductions.
See our FAQ to understand “What deductions are available to producers under the Blue Box Regulation?”
-
There are only two allowable deductions for Blue Box materials. There are for materials that are:
- collected from an eligible source at the time a related product was installed or delivered (e.g., packaging that is removed from the house by a technician installing a new appliance). This is the “installation deduction”.
- deposited into a receptacle at a location that is collected from a business or institution where Blue Box collection services are not provided under the regulation. This is the “ineligible source deduction” that was expanded by the regulation amendment in July 2023.
Ineligible source deductions:
Blue Box Producers may deduct materials that are collected from a business or institution where producers are not required to provide Blue Box collection services. Examples include offices, stores and shopping malls, restaurants, community centres, recreation facilities, sports and entertainment venues, universities and colleges, and manufacturing facilities.
Producers cannot deduct the following materials collected through the collection systems established under the Blue Box Regulation:
- Material that is generated at a facility (including multi-residential buildings, retirement homes, long-term care homes and schools).
- Material that is collected from a residence through a curbside or depot collection service.
- Material that is collected from a public space (including an outdoor area in a park, playground or sidewalk, or a public transit station).
- Material collected under an alternative or supplemental collection system.
- Beverage containers cannot be deducted.
Materials that are deducted cannot count toward a producer’s management requirement.
Please see the Reporting Guidance Ineligible Source Deductions for the 2024 Blue Box Supply Report for more information on how to determine and use these deductions.
-
Yes, there are some key changes to the data reported to Stewardship Ontario and what needs to be reported under the new regulation, which may affect what a producer is obligated for and should be considered if using data previously reported to Stewardship Ontario:
- There are fewer reporting categories than under the Stewardship Ontario program
- Certified compostable packaging and products now must be reported separately, but this category does not have management requirements
- There are only two deductions permitted under the Blue Box Regulation, and producers must report total supply and then report any weight to be deducted separately
- Exemptions are based on tonnage supply under each material category instead of a total supply weight threshold of less than 15 tonnes as in Stewardship Ontario’s program
See our FAQ to understand “What deductions are available to producers under the Blue Box Regulation?”; “Are there exemptions for Blue Box producers?“; “Are there any differences in Blue Box producer hierarchies between the current Stewardship Ontario program and the new Blue Box Regulation?”; and “Are there are any differences in obligated Blue Box materials between the current Stewardship Ontario program and the new Blue Box Regulation?”
-
Public sector institutions, such as colleges and universities, are suppliers of Blue Box materials to consumers in Ontario. They supply Blue Box materials to consumers on-site (e.g., food service packaging, unprinted paper in photocopiers, etc.) and off-site (e.g., mailings).
For the purposes of supply reporting, colleges, universities, and other public sector institutions must determine the total amount of Blue Box material they supply to consumers in Ontario. One way to gather this data is by canvassing internal departments to obtain annual weights of Blue Box materials supplied to consumers on-site and off-site.
Also see:
FAQ: What deductions are available to producers under the Blue Box Regulation?
Compliance Bulletin: What Blue Box materials need to be reported?