
Frequently Asked Questions
Results (117)
Click the question to read the answer.
-
Under the Blue Box Regulation, there are three types of exemptions that apply to producers:
- Based on a producer’s gross annual revenue,
- based on the weight of Blue Box materials supplied into Ontario, and
- for producers of newspaper
1. Any producer whose gross annual Ontario revenue from products and services is less than $2,000,000 is exempt from all producer requirements under the regulation. In the case where the producer is a franchisor, it is the gross annual revenue of the system that is used to determine if an exemption applies.
Any producer who meets the exemption must keep any records that demonstrate its gross annual Ontario revenue is less than $2,000,000 in a paper or electronic format that can be examined or accessed in Ontario for a period of five years from the date of creation.
See our FAQs to understand what revenues municipalities and registered charities should consider when determining whether or not they are an exempt producer.
2. A producer who is above the revenue-based exemption level may still be exempt from performance requirements (collection, management and promotion and education) if their supply weight is below the exemption levels outlined in the table below.
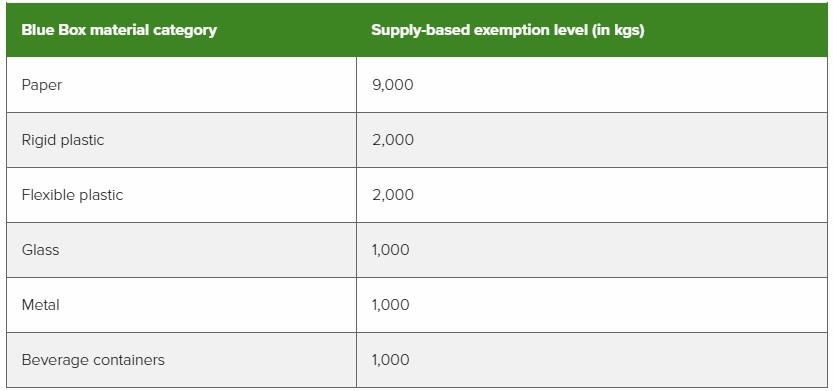
If a producer’s annual revenue is more than $2,000,000 and supply weight in all material categories is less than the tonnage exemption threshold, the producer is required to register and report.
If a producer’s annual revenue is more than $2,000,000 and supply weight in at least one material category is above the tonnage exemption threshold, the producer is required to meet all obligations (registration, reporting, collection, management, and promotion and education). However, producers are only required to meet their minimum management requirement in material categories where they are above the exemption level.
3. As outlined in the amended Blue Box Regulation (released April 19, 2022), producers of newspapers may be exempt from collection, management, and promotion and education requirements. For the purposes of this exemption, “newspapers” includes newspapers and any protective wrapping and any supplemental advertisements and inserts that are provided along with the newspapers.
For a producer to qualify for this exemption, newspapers must account for more than 70% of their total weight of Blue Box materials supplied to consumers in Ontario in a calendar year. If exempt, the producer is not required to meet collection, management, and promotion and education requirements for all Blue Box materials they supply in Ontario in the following two calendar years.
A producer whose newspaper supply accounts for 70% or less of their total weight of Blue Box materials is subject to collection, management, and promotion and education requirements for all Blue Box materials they supply in Ontario.
-
A lighting producer qualifies for an exemption if their average weight of supply for that calendar year is less than or equal to 700 kg.
Average supply weight is determined using the following formula:
Average weight of lighting supply = (Y3 + Y4 + Y5) / 3
Eg. 2025 average weight of supply = (2022 + 2021 + 2020) / 3
Lighting producers that meet the exemption criteria are exempt from:
- Registering with and reporting to RPRA
- Establishing a collection and management system
- Meeting a management requirement
- Promotion and education requirements
Producers must verify that they continue to meet the exemption annually, since their average weight of supply will change from year to year.
Producers that are exempt must keep records of the materials they supplied, as set out in section 30 of the regulation.
Producers are advised to confirm their exemption with the Compliance Team at 833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
See our FAQs: “How are lighting producers’ minimum management requirements determined?” and “What do I have to do if I am an exempt lighting producer?”
-
An HSP producer qualifies for an exemption if their average weight of supply for the previous calendar year is less than or equal to the weight specified in the chart below:
Exempt (Less than <) Oil Filters 3.5 Non-refillable Pressurized Containers 3 Antifreeze 20 Oil Containers 2 Solvents 3 Paints and Coatings 10 Pesticides 1 Refillable Pressurized Containers N/A Mercury-containing Devices Fertilizers Propane Containers (refillable) See our FAQ “Am I a small, large, or exempt HSP producer?” to determine how to calculate if you are an exempt HSP producer.
HSP producers that meet the exemption criteria are exempt from:
- Registering and reporting to RPRA
- Establishing a collection and management system
- Meeting a management requirement
- Promotion and education requirements
Producers must verify that they continue to meet the exemption annually, since their average weight of supply will change from year to year.
Exempt producers must keep records related to the weight of HSP supplied into Ontario each year and provide them to RPRA upon request.
Producers are advised to confirm their exemption with the Compliance Team at 1-833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
-
A battery producer qualifies for an exemption if their average weight of supply for that calendar year is:
- Less than or equal to 2,500 kg of rechargeable batteries, or
- Less than or equal to 5,000 kg of primary batteries.
Average supply weight is determined using the following formula:
Average weight of rechargeable batteries = (Y3 + Y4 + Y5) / 3
- Eg. 2025 average weight of supply = (2022 + 2021 + 2020) / 3
Average weight of primary batteries = (Y2 + Y3 + Y4) / 3
- Eg. 2025 average weight of supply = (2023 + 2022 + 2021) / 3
Battery producers that meet the exemption criteria are exempt from:
- Registering and reporting to RPRA.
- Establishing a collection and management system.
- Meeting management requirements.
- Promotion and education requirements.
Producers must verify that they continue to meet the exemption annually, since their average weight of supply will change from year to year.
Exempt producers must keep records related to the weight of batteries (by category) supplied into Ontario each year and provide them to RPRA upon request.
Producers are advised to confirm their exemption with the Compliance Team at 833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
Also see our FAQ: ‘How are battery producers’ minimum management requirements determined?‘
-
An ITT/AV producer qualifies for an exemption if their average weight of supply for that calendar year is less than or equal to 5,000 kg.
Average supply weight is determined using the following formula:
Average weight of ITT/AV supply = (Y3 + Y4 + Y5) / 3
Eg. 2025 average weight of supply = (2022 + 2021 + 2020) / 3
ITT/AV producers that meet the exemption criteria are exempt from:
- Registering and reporting to RPRA
- Establishing a collection and management system
- Meeting a management requirement
- Promotion and education requirements
Producers must verify that they continue to meet the exemption annually, since their average weight of supply will change from year to year.
Exempt producers must keep records related to the weight of ITT/AV supplied into Ontario each year and provide them to the RPRA upon request.
Producers are advised to confirm their exemption with the Compliance Team at 833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
-
A tire producer qualifies for an exemption if their average weight of supply for that calendar year is less than 1,175 kg.
Average supply weight is determined using the following formula:
Average weight of tire supply = (Y3+Y4+Y5) / 3
E.g. 2025 average weight of supply = (2022 + 2021 + 2020) / 3
Tire producers that meet the exemption criteria are exempt from:
- Registering and reporting to RPRA
- Establishing a collection and management system
- Meeting a management requirement
Producers must verify that they continue to meet the exemption annually, since their average weight of supply will change from year to year.
Exempt producers must keep records related to the weight of tires supplied into Ontario each year and provide them to RPRA upon request.
Producers are advised to confirm their exemption with the Compliance Team at 833-600-0530 or registry@rpra.ca.
-
Lighting is defined as electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) that has the primary purpose of producing light.
Note, the below lists are non-exhaustive.
Lighting does not include:
- lighting that is provided with another product or a fixture, or
- lighting that also falls into the category of ITT/AV.
Examples of included lighting under the EEE Regulation:
- Bulbs
- Dimmable light bulb
- Fluorescent bulb
- Halogen bulb
- Headlight bulb
- High intensity discharge (HID) lamp
- Indicator Lights
- Incandescent bulb
- Lamp
- Light emitting diode (LED) bulb
- Mini and miniature bulbs
- Motion activated bulb
- Replacement bulbs & lamps
- Tube light
- UV Lamps
- Wi-Fi light bulb
Examples of excluded lighting under the EEE Regulation:
- Ceiling light
- Chandelier
- Flashlights
- Floor lamp
- Flush mount light
- Light bulb supplied with a fixture
- Light bulb supplied with a product
- Light Strips
- Pendant light
- Recessed lighting
- Ring lights
- Sconce
- String lights
- Table & floor lamps
-
- A lighting hauler is a person that arranges the transport of lighting used in Ontario that are destined for processing, reuse, refurbishing or disposal.
- A lighting refurbisher is a person that prepares or refurbishes lighting used in Ontario for the purpose of reuse.
- A lighting processor is a person that processes lighting used in Ontario for the purpose of resource recovery.
-
As of January 1, 2023, lighting producers are required to establish and operate a lighting collection system that meets the accessibility requirements in the EEE Regulation. A producer must ensure that all lighting collected is managed regardless of what their minimum management requirements is.
A producer has the choice of establishing and operating their own collection and management systems or working with one or more producer responsibility organizations (PROs) registered with the Authority to meet their obligations.
For detailed information on lighting producer requirements, visit our Lighting Producer webpage.
If you have further questions about lighting producer requirements, contact the Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or 1-833-600-0530.
-
There is an exemption in the Blue Box regulation for producers whose gross annual revenue generated from products and services in Ontario less than $2 million. The revenue that counts towards the exemption is revenue from products and services. Charitable donations are not revenue from products and services and therefore does not count towards the exemption. Revenue other than charitable donations that are recorded from registered charities will be considered revenue from products and services.
-
Yes. The new Subject Waste Program Regulation under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016, preserves and clarifies existing Hazardous Waste Program fee exemptions, which RPRA must follow when recovering the cost to operate the HWP Registry.
Existing exemptions include:
- Municipal hazardous or special waste
- Contaminated sites
- Emergencies (spills)
- Tonnage-fee exempt recycling facilities
-
A person is considered a lighting producer under the Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) Regulation if they supply lighting into Ontario and:
- Are the brand holder for the lighting and have residency in Canada;
- If there is no resident brand holder, have residency in Ontario and import lighting from outside of Ontario;
- If there is no resident importer, have residency in Ontario and market directly to consumers in Ontario (e.g. online sales); or
- If there is no resident marketer, do not have residency in Ontario and market directly to consumers in Ontario (e.g., online sales).
Even if you do not meet the above definition, there may be circumstances where you qualify as a producer. Read the Electrical and Electronic Equipment Regulation for more detail or contact the Compliance and Registry Team for guidance at registry@rpra.ca or (647) 496-0530 or toll-free at (833) 600-0530.
See our FAQ to understand “What is lighting under the EEE Regulation?”, “Who is a brand holder?”
-
Yes, there are some key changes to the data reported to Stewardship Ontario and what needs to be reported under the new regulation, which may affect what a producer is obligated for and should be considered if using data previously reported to Stewardship Ontario:
- There are fewer reporting categories than under the Stewardship Ontario program
- Certified compostable packaging and products now must be reported separately, but this category does not have management requirements
- There are only two deductions permitted under the Blue Box Regulation, and producers must report total supply and then report any weight to be deducted separately
- Exemptions are based on tonnage supply under each material category instead of a total supply weight threshold of less than 15 tonnes as in Stewardship Ontario’s program
See our FAQ to understand “What deductions are available to producers under the Blue Box Regulation?”; “Are there exemptions for Blue Box producers?“; “Are there any differences in Blue Box producer hierarchies between the current Stewardship Ontario program and the new Blue Box Regulation?”; and “Are there are any differences in obligated Blue Box materials between the current Stewardship Ontario program and the new Blue Box Regulation?”
-
A producer’s management requirement is how much Blue Box material they must ensure is collected and processed into recovered resources each year. Management requirements are calculated based on what they supplied into Ontario one year prior and the resource recovery percentage as set in the regulation. A producer’s management requirement is calculated separately for each Blue Box material category (beverage container, glass, flexible plastic, rigid plastic, metal and paper).
Some producer are exempt from having a management requirement based on their supply data, for more information on exemptions see the FAQ Are there exemptions for Blue Box producers? A producer that does not have a management requirement does not have any collection, management or promotion and education obligations.
A producer with a management requirement must also provide collection and promotion and education services in Ontario. Most producers will contract the services of a producer responsibility organization (PRO) to meet their collection, management and promotion and education obligations.
To view your management requirement(s), log into your registry account, download a copy of your Blue Box Supply Report and review the section with your minimum management requirements. Management requirement for a given year are determine by supply data from two years prior. For example, 2023 management requirements were based on 2021 supply data (submitted in producers’ 2022 Supply Report).
Unsure if you are a Blue Box producer? See our FAQs Am I a producer of Blue Box product packaging? And Am I a producer of paper products and packaging-like products?
-
A newspaper producer is a person who supplies newspapers to consumers in Ontario. For the purpose of the Blue Box Regulation, newspapers include broadsheet, tabloid or free newspaper. For further information, see the FAQ: What is a newspaper?
Note that a producer of supplemental advertisements or flyers that are supplied with a newspaper would not be considered a newspaper producer as they do not supply the actual broadsheet, tabloid, or free newspaper. This producer cannot use the newspaper exemption percentage to be exempt from Blue Box collection and management requirements. See the FAQ: Are there exemptions for Blue Box producers?
-
An exempt producer is not required to:
- Register and report to RPRA
- Establish a collection and management system
- Meet a management requirement
- Meet promotion and education requirements
Exempt producers must retain records related to the weight of lighting supplied into Ontario each year and provide them to RPRA upon request.
See our FAQ: ‘How do I determine if I am an exempt lighting producer?’
-
A producer’s individual minimum management requirement is determined by the following formulas, found in section 14 of the Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) Regulation, summarized in the following chart:
Performance Year Supply Report Year Formula 2025 2024 (2020 supply + 2021 supply + 2022 supply) / 3×30% 2026 2025 (2021 supply + 2022 supply + 2023 supply) / 3×30% 2027 2026 (2022 supply + 2023 supply + 2024 supply) / 3×30% 2028 2027 (2023 supply + 2024 supply + 2025 supply) / 3×30% 2029 2028 (2024 supply + 2025 supply + 2026 supply)/ 3×30% 2030 2029 (2025 supply + 2026 supply + 2027 supply)/ 3×30% 2031 2030 (2026 supply + 2027 supply + 2028 supply)/ 3×35% It is important to note that producers must ensure that all lighting that is collected is managed, regardless of their minimum management requirement.
Note: Producers with a management requirement below a certain threshold may be exempt from registering with and reporting to RPRA. See our FAQ ‘How do I determine if I am an exempt lighting producer?’ to learn more.
-
Lighting producers report supply data in kilograms from two years prior (i.e., 2023 supply data is reported in 2025) in their annual supply report.
Producers can use the actual weight of the obligated lighting, or RPRA’s weight conversion factors found in the EEE Verification and Audit Procedure.
For further questions, contact the Compliance Team at registry@rpra.ca or 1-833-600-0530.
-
The Manage PRO option will appear on the dashboard below your list of supply data reports when your supply data reporting is complete and if you have management requirements. If your supply data reporting is below the supply exemption threshold you will not have management requirements, and therefore not need to assign a PRO to assist with your obligations.
Also note that Account Admin are the only portal users that can manage your PRO’s responsibility, so this widget is not viewable to primary and secondary users.
-
No, where a producer is exempt, the regulatory obligations do not become the responsibility of the organization that is next in the producer hierarchy. The exempt producer remains the “producer” for those materials; they are just exempt from certain requirements under the regulation as set out in the relevant provisions providing for the exemption. This is the case in all RRCEA regulations.
-
There is an exemption in the Blue Box Regulation for producers whose gross annual revenue generated from products and services in Ontario is less than $2 million. The following sources are excluded for the purpose of determining revenue:
- Government tax revenue
- Property taxes
- General assistance funding received under the Ontario Municipal Partnership Fund
- Payments in lieu of taxes
- Canadian or Ontarian government grants available to municipalities with the intent of investing in public infrastructure
-
The regulation requires notices to be filed for three types of activities:
1. Notice filings for excess soil from Project Areas that can be made by a Project Leader or Authorized Person and may require retaining a Qualified Person. These notices will be required starting January 1st, 2022, before soil that will become excess soil is removed from the Project Area. There will be two fillings for each notice:
- An initial filing before the soil is removed, which will require the following information to be provided:
-
- a description of the project and Project Area including the location of each property within the project area
- the contact information of the Project Leader, Operator or Authorized Person and the person responsible for transportation, and if applicable, the qualified person
- an estimated amount of the soil that will be generated broken down by quality standard
- a list of substances/materials that were added to the soil
- the location of temporary or final sites that the soil will be transported to
- details of the Reuse Site(s) where the soil will be moved to
- information on any peer review or certification processes if applicable
- and a declaration by the Project Leader.
Exceptions
The Project Leader, Operator or Authorized Person may file a notice after soil that will become excess soil has been removed from the project area if:
- conducting the required sampling and analysis at the project area is impractical
- the soil is removed from the project area and delivered to a temporary site to conduct the required sampling, and
- the Project Leader, Operator or Authorized Person makes sure the required sampling is conducted as soon as the soil is delivered to the temporary site
If soil is removed before a notice is filed in the Registry, the Project Leader, Operator, or Authorized Person is required to ensure that the notice is filed in the Registry before the soil that has become excess soil is transported from the temporary site to the final site.
More information about when this type of notice filing is not required can be found under Schedule 2 of the regulation.
The Project Leader or Authorized Person is required to update notice filings that are no longer complete or accurate within 30 days after the day the person becomes aware that the information is no longer complete or accurate.
2. A final notice within 30 days after excess soil has been removed from the Project Area or temporary site which will require the following information:
- the amount of excess soil removed from the Project Area that was deposited at: a class 1 soil management site, a class 2 soil management site, a reuse site, a local waste transfer facility, and a landfilling site or dump
- the date on which the last load of excess soil was removed from the project area or temporary site
- a declaration by the Project Leader
2. Notice filings for Residential Development Soil Depots can be made by an Owner, Operator, or Authorized Person. This notice will be required before excess soil is deposited on a residential development soil depot site if the depot commences operation on or after January 1, 2022, or if the depot was already in operation when the requirement to file a notice comes into effect, the notice should be filed ahead of January 1, 2022.
The Owner or Operator of the Residential Development Soil Depot must ensure that the quality of the excess soil accepted and managed at the depot meets the applicable Excess Soil Quality Standards set out in the regulation. There will be two filings for each notice:
- An initial filing before the soil is received, which will require the following information to be provided:
- the site location
- the contact information of the Site Owner and Operator
- the project commencement date
- the estimated amount of soil (including inventory on-site)
- the site instrument identification
- and a declaration by the Site Owner or Operator.
- A final filling within 90 days of the depot closing indicating the date when the depot ceased operations, and a declaration by the Site Owner or Operator.
3. Notice filings for Reuse Sites can be made by a Site Owner, Operator, or an Authorized Person. These will be required starting January 1st, 2022, and apply to a Reuse Site that expects at least 10,000 m3 of excess soil to be deposited after January 1st, 2022 (including Reuse Sites that were in operation before that date). There will be two filings for each notice:
- An initial filing before the excess soil is deposited, which will require the following information to be provided:
- the site location/property type
- the contact information of the Site Owner and Operator
- a description of the undertaking
- the applicable excess soil quality standards for the site
- the estimated amount of soil by quality standard
- the estimated dates when the first and last soil load will be deposited
- the site instrument identification
- and a declaration by the Site Owner or Operator.
- A final notice filing within 30 days after the final load of excess soil has been deposited at the Reuse Site which will require the following information:
- confirmation that all excess soil that will be reused for a beneficial purpose has been deposited at the reuse site
- the total amount of excess soil that was deposited
- the date the final load of excess soil was deposited
- and a declaration by the owner or operator.
The Site Owner or Operator is required to update notice filings that are no longer complete or accurate within 30 days after the day the person becomes aware that the information is no longer complete or accurate.
Exemptions:
Reuse Sites that are part of infrastructure projects are not required to file notices.
-
Yes, in October 2022, RPRA has migrated the facility and waste stream data identified below to the new registry to minimize the volume of data users would otherwise have to enter from scratch.
Data that has been migrated into the Registry from HWIN includes:
- Active generators accounts:
- Generator ID
- Company details
- Site location
- Company official / alternate HWIN Administrator details
- Site Details
- Waste Identification (for active wastes):
- Waste Class
- Waste Stream
- Land Disposal Restrictions (LDR) Notification Form
- Fee exemptions
- Carrier and Receiver Environmental Compliance Approval (ECA) information:
- ECA number
- Company Name
- Site location
- Company admin / official information
- Waste codes
*The following data has not been migrated:
- Generator accounts where the generator number or ID begins with ONR or ONF
- Inactive waste streams and facilities
- Manifests
- On-site processing, storage and disposal information
- LDR questionnaires (only LDR notification forms will be migrated)
- Financial information (including account balances, payment information)
- Document attachments (such as copies of Environmental Compliance Approvals)
Note: while some recently expired generator accounts might have been migrated to the registry, users should have ensured that their data in the HWIN system is accurate and up to date ahead of the migration in October to ensure their data is accessible in the registry. This may have included reactivating inactive waste streams and facilities in HWIN in order for them to be migrated to the registry.
-
Fees are tied to the activities that generators report on or that are reported on their behalf by authorized generator delegates (AGDs) (e.g., manifests and on-site storage, processing and disposal). Fees will be invoiced on the first day of each month and will include all manifests completed in the previous month.
RPRA consulted industry stakeholders on the 2025 HWP Registry Fees from September 27 to November 12, 2024 and, based on the feedback received, the HWP Registry Fees have been set on the following basis:
- fees is charged to generators only, aligning with the current Hazardous Waste Program fee structure
- the manifest fee has been set at $6, the same rate as today, and will be charged per manifest
- the tonnage fee has been set at $27.50, instead of the past $30 fee, and will only apply to shipped hazardous waste and hazardous waste that is disposed on site which remains the same as today’s framework
- there is no annual registration fee
- all existing fee exemptions are maintained, as per Ontario Regulation 323/22: Subject Waste Program
View the 2025 HWP Registry Fees Schedule
See FAQ: Will I pay my fees using a prepaid account like HWIN?
-
RPRA consulted industry stakeholders on the 2025 HWP Registry Fees from September 27 to November 12, 2024 and, based on the feedback received, the HWP Registry Fees have been set on the following basis:
- fees will be charged to generators only, aligning with the current Hazardous Waste Program fee structure
- the manifest fee will be set at $6, the same rate as today, and will be charged per manifest
- the tonnage fee has been set at $27.50, instead of the current $30 fee, and will only apply to shipped hazardous waste and hazardous waste that is disposed on site which remains the same as today’s framework
- there will be no annual registration fee
- all existing fee exemptions will be maintained, as per Ontario Regulation 323/22: Subject Waste Program
-
Registry Resources such as Registry Procedures, Compliance Bulletins, and Reporting Guides can be found on our Lighting Registry Resources webpage.
-
Here are the lists of registered PROs:
Hazardous and Special Products PROs
These lists will continue to be updated as new PROs register with RPRA.
-
For the purposes of the Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) Regulation, a fixture is an electrical device supporting one or several electric lamps that provide illumination. Fixtures are not obligated as lighting under the EEE Regulation.
Fixtures require an electrical connection to a power source, whether it is directly connected to alternative current or batteries.
Fixtures can be hardwired, free standing, portable and even solar powered.
Examples of fixtures include table lamps, floor lamps, etc.
-
RPRA has developed a library of resources to support Registry users navigate the online system and meet their regulatory requirements. RPRA consistently adds to this pool of resources based on upcoming requirements, emerging needs, and questions we receive from stakeholders.
View Registry resources for each program:
-
RPRA’s Where to Recycle map displays locations across Ontario where the public can drop off used materials to be recycled, such as batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste (e.g., paint, antifreeze, pesticides), lighting and tires, for free. Materials collected at these locations are reused, refurbished, recycled, or properly disposed of to help keep them out of landfill, recover valuable resources and protect our environment. Learn more here.
-
The Where to Recycle map displays locations that the public can drop off used materials to be recycled, such as batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste (e.g., paint, antifreeze, pesticides), lighting and tires, for free. For specific examples of materials accepted and important information to know before dropping off materials, visit the Where to Recycle map.
-
Under Ontario’s circular economy laws, businesses that produce or supply batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste, lighting, and tires are required to provide recycling locations and report them to RPRA. Only locations reported to RPRA appear on the map.
Recycling locations you’re already aware of that don’t appear on the map most likely collect materials not listed above or are operated by a municipality who aren’t required to report recycling locations to RPRA.
-
Collection sites for batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste, lighting, and tires that are reported by producers, or PROs on their behalf, appear on the map.
Collection sites that are considered private (e.g. a recycling bin inside a business that is not accessible to the public) do not appear on the map.
-
Battery, electronics, lighting and tire collection sites must be operated during regular business hours throughout the calendar year.
Household hazardous waste collection sites may open seasonally. The Where to Recycle map should reflect the time of the year when the collection site operates.
-
Blue Box materials (i.e., products and packaging made of metal, glass, paper, flexible plastic, rigid plastic, and beverage containers) are typically collected directly from residences through the provincial Blue Box Program. RPRA’s Where to Recycle map displays public locations for recycling materials that don’t belong in your Blue Box (e.g., batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste, lighting and tires).
For more information on recycling Blue Box materials, visit Circular Materials’ website. Circular Materials is the administrator of Ontario’s Blue Box collection system.
-
This map provides locations for most materials captured under Ontario’s recycling programs, which are overseen by RPRA: batteries, electronics, household hazardous waste, lighting and tires. See below for more information on what to do with materials that aren’t displayed on the map.
Household hazardous waste
Drop-off locations for some household hazardous waste, such as refillable propane containers, refillable pressurized containers, fertilizers and mercury-containing thermostats, thermometers and barometers, aren’t displayed on the map because they aren’t required (under the recycling program) to be reported to RPRA.
However, there may be locations that accept these materials for recycling that aren’t listed on RPRA’s Where to Recycle map. To find a location to dispose of refillable propane containers, refillable pressurized containers, fertilizers or mercury-containing thermostats, thermometers and barometers, contact one of the businesses below or visit their website:
- Mobius PRO Services
- Offers services for refillable propane containers and refillable pressurized containers
- Phone: 833-266-2487 | Email: info@mobiuspro.ca | Website
- Product Care Association
- Offers services for fertilizers and refillable propane containers
- Website (includes a map with recycling locations)
- Ryse Solutions Ontario Inc.
- Offers services for fertilizers, refillable pressurized containers, refillable propane containers, barometers, thermometers and thermostats
- Phone: 289-352-1200 | Email: info@ryseinc.ca | Website
- Tank Traders
- Offers services for refillable propane containers
- Website (includes a map with recycling locations)
- Thermostat Recovery Program
- Offers services for thermostats
- Website (includes a map with recycling locations)
Other materials (e.g., organics, mattresses, textiles, etc.)
If you need to recycle materials outside of the programs that RPRA oversees (e.g., organics, mattresses, textiles, etc.), please contact the waste management department at your municipality for proper disposal instructions.
-
When paying fees to RPRA, you can select from one of the following payment methods:
- Bank withdrawal (pre-authorized debit)
- Credit card
- Electronic data interchange (EDI; also commonly known as ACH or EFT)
- Electronic bill payment
- Cheque
For instructions on how to submit payment by the method you chose, read one of the following FAQs:
- How do I pay my fees to RPRA by credit card?
- How do I pay my fees to RPRA by bank withdrawal (pre-authorized debit)?
- How do I pay my fees to RPRA by electronic bill?
- How do I pay my fees to RPRA by cheque?
- How do I pay my fees to RPRA by electronic data interchange (EDI)?
To note, Registry invoices are considered due on receipt. Invoices are in CAD funds and payments must be sent in CAD.
-
We recommend using Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge or Apple Safari when accessing the Registry. If you are experiencing an issue with the Registry, try clearing your cache or updating the browser to the latest version.
If you are using a different browser, the Registry will not function.
-
You should use the address where you carry on business. If you carry on business in more than one location in Ontario, use the main address for your business in Ontario. If you do not have an Ontario address, use the address that relates to the activities you carry out in Ontario.
-
Yes. PROs are private enterprises and charge for their services to producers.
Each commercial contract a producer enters with a PRO will have its own set of terms and conditions. It is up to the PRO and producer to determine the terms of their contractual agreement, including fees and payment schedule.
RPRA does not set the terms of the contractual arrangements between PROs and producers.
-
No. A PRO cannot report on behalf of service providers.
-
Yes. Producers and service providers can enter into contractual agreements with multiple PROs.
-
Program fees are charges that producers obligated under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016, are required to pay to RPRA annually to recover its operational costs, including costs related to building and operating the registry, providing services to registrants, and compliance and enforcement activities.
All current and past fee schedules can be found here.
-
To register as a PRO, contact the Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or call 647-496-0530 or toll-free 1-833-600-0530.
-
Under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, the Authority is required to provide an annual report to the Minister that includes information on aggregate producer performance, and a summary of compliance and enforcement activities. Under section 51 of the Act, the Registrar also is required to post every order issued on the Registry.
-
A producer responsibility organization (PRO) is a business established to contract with producers to provide collection, management, and administrative services to help producers meet their regulatory obligations under the Regulation, including:
- Arranging the establishment or operation of collection and management systems (hauling, recycling, reuse, or refurbishment services)
- Establishing or operating a collection or management system
- Preparing and submitting reports
PROs operate in a competitive market and producers can choose the PRO (or PROs) they want to work with. The terms and conditions of each contract with a PRO may vary.
-
No. The Authority does not administer contracts or provide incentives. Under the Regulations, producers will either work with a producer responsibility organization (PRO) or work directly with collection sites, haulers, refurbisher’s and/or processors to meet their collection and management requirements. Any reimbursement for services provided towards meeting a producers’ collection and management requirements will be determined through commercial contracts.
To discuss any payment, contact your service provider or a PRO. RPRA does not set the terms of the contractual arrangements between PROs and producers.
-
Resident in Ontario means a person having a permanent establishment in Ontario within the meaning of the Corporations Tax Act. A permanent establishment is usually a fixed place of business such as an office, factory, branch, warehouse, workshop, etc. In some cases, a corporation will be deemed to operate a permanent establishment in Ontario. These include cases where:
- The corporation produced, grew, mined, created, manufactured, fabricated, improved, packed, preserved or constructed anything in the province, in whole or in part;
- The corporation carries on business through an employee or agent in the province who has general authority to contract for the corporation; or
- The corporation carries on business through an employee or agent in the province who has a stock of merchandise owned by the corporation from which they regularly fill orders that they receive.
- A corporation will also have a permanent establishment in Ontario if it uses substantial machinery or equipment in the province, or if it is has a permanent establishment elsewhere in Canada and owns land in the province.
For more details about what constitutes a permanent establishment, see the definition of “permanent establishment” in the Corporations Tax Act.
-
To create a Registry account with the Authority, you will need to provide:
- CRA Business Number (BN)
- Legal Business Name
- Business address and phone number
- Address of where you work (if different from the main office)
- Contact information for your billing contact (this may also be added later)
-
For regulatory purposes, we need to know your legal name — the name you are incorporated under. We also need to know your business operating name if it is different from your legal business name to add to our published list of registrants. The list of registrants will be available on our website to allow registrants to interact with one another and to provide information to the public.
For example, if you are a registered collector and your legal name is 123456789 Ontario Ltd. and your business operating name is “Jack’s Garage,” a member of the public looking for a place to drop off used tires will need to know the name you are operating under to identify your location.
-
Brand holders and producers that supply products and packaging are required by legislation to meet individual mandatory collection and resource recovery requirements and may face compliance and enforcement consequences for failing to do so. The executive attestation ensures that executives responsible for managing the brand holder’s or producer’s business are aware of these requirements and can ensure that appropriate measures are put in place to achieve compliance with the regulations.
-
Individual Producer Responsibility (IPR) means that producers are responsible and accountable for collecting and managing their products and packaging after consumers have finished using them.
For programs under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 (RRCEA), producers are directly responsible and accountable for meeting mandatory collection and recycling requirements for end of life products. With IPR, producers have choice in how they meet their requirements. They can collect and recycle the products themselves, or contract with producer responsibility organizations (PROs) to help them meet their requirements.
-
The Authority is the regulator designated by law to oversee the operation and wind up of current waste diversion programs under the Waste Diversion Transition Act, 2016. The Authority provides oversight, compliance, and enforcement activities with respect to regulations made under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016.
-
The Authority recognizes the commercially sensitive nature of the information that parties submit to the registry. The Authority is committed to protecting the commercially sensitive information and personal information it receives or creates in the course of conducting its regulatory functions. In recognition of this commitment, the Authority, in addition to the regulatory requirements of confidentiality set out in the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act 2016 (section 57), has created an Access and Privacy Code that applies to its day-to-day operations, including the regulatory functions that it carries out.
Obligated material supply, collection, and resource recovery data will only be made public in aggregate form, to protect the confidentiality of commercially sensitive information.
The Authority will publish the names and contact information of all registered businesses – producers, service providers (collectors, haulers, processors, etc.), and producer responsibility organizations. The public will also have access to a list or method to locate any obligated material collection sites, as this information becomes available.
As part of its regulatory mandate, the Registrar will provide information to the public related to compliance and enforcement activities that have been undertaken.
The information that is submitted to the Registry will be used by the Registrar to confirm compliance and to track overall collection and management system performance. It will also be used by the Authority to update its policies and procedures and by the Ministry of Environment, Conservation and Parks for policy development.
-
In accordance with the legislation (Resource Recovery Circular Economy Act 2016, section 57), the Authority is required to comply with strict confidentiality requirements. The Authority has also developed an Access and Privacy Code that applies to its day-to-day operations.
The Registry has been developed according to cybersecurity best practice principles. This includes VPN-based restrictions, staff training on all cybersecurity policies, staff access to the Registry on a strict role-requirement basis, and registry interface security features (example: two-factor authentication).
-
Yes. If you are a producer with retailers or distributors supplying your obligated EEE into Ontario, you can email us at registry@rpra.ca to discuss options on how to report your supply data. There are several options available, including an easy-to-use sales formula and weight conversion factors. See the EEE Verification and Audit procedure for more information.
One option is to have your supply data reported by each of your retailers or distributors on a piecemeal basis. The piecemeal option requires that extra steps be undertaken by you and the Authority. You must contact the Authority in advance if you wish to pursue this option.
Note that even if you have a retailer or distributor providing data on your behalf, it remains the producer’s obligation to ensure that all the required data gets reported and that it is reported accurately to the Authority in accordance with the EEE Regulation. The entry of inaccurate information by someone on your behalf is not a defense to non-compliance.
-
Yes. You are still required to register with the Authority Registry even if you already have an existing account.
-
Businesses have the choice to recover the cost of recycling their products by incorporating those costs into the overall cost of their product (as they do with other costs, such as materials, labour, other regulatory compliance costs, etc.) or by charging it as a separate fee to consumers.
Environmental fees are not mandatory and are applied at the discretion of the business charging them, including the amount of the fee.
-
Consumer protection laws in Ontario prohibits the misrepresentation of charges, which means that producers or retailers cannot misrepresent any visible fees as a regulatory charge, tax, RPRA fee or something similar. Consumers who have questions or concerns about a specific transaction or want to report a misrepresentation can contact the Ministry of Public and Business Service Delivery at 1-800-889-9768.
As of March 2023, the promotion and education requirements related to environmental fees have been removed from the Tires, Batteries, Electrical and Electronic Equipment, and Hazardous and Special Products regulations. No changes were made to the Blue Box Regulation as it never contained promotion and education requirements related to these fees.
RPRA’s compliance bulletin Charging Tire Fees to Consumers has since been revoked and RPRA has ceased its enforcement of promotion and education requirements for visible fees across all materials.
-
There is no set environmental fee for any product, the amount of the fee charged is decided by the business.
-
No. An environmental fee is not a government tax and cannot be represented as mandatory, a regulatory charge, or a RPRA fee. It is a fee charged at the discretion of a business to recover their costs related to recycling the product.
-
If you are concerned about the fee you were charged, you should contact the business that charged you the fee to request a more detailed explanation of how the fee was determined.
-
As the Regulator responsible for enforcing regulations under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016, the Registrar uses their discretion for when it is necessary to give registrants more time to collect the information needed for registration and/or reporting.
-
RPRA does not vet PROs before listing them on the website. Any business that registers as a PRO will be listed. Producers should do their own due diligence when determining which PRO to work with.
-
Account Admins must add any new, or manage existing, Primary Contacts under the program they wish to give them access to in order for the Primary Contact to be able to submit a report (e.g., permissions to view and complete reports).
To Manage contacts on your Registry account, please see the following steps:
- Log into your account
- Once you are logged in, click on the drop-down arrow in the top right corner and select Manage Users
- Under Actions, click Manage to update preferences of existing users
- Click Add New User to add an additional contact to your account
- To give reporting access to a Primary Contact, select the program from the drop-down that you would like to grant them access to
-
In determining whether an obligated producer used best efforts to meet their management requirements, the Compliance Team will consider whether the producer, acting in good faith, took all reasonable steps to meet the requirements outlined in the applicable regulation.
For example, best efforts in the context of management requirements may involve a producer regularly monitoring the volume of material being collected and managed, and implementing plans for increasing those volumes if the requirements are unlikely to be met.
Producers can contact the Compliance Team to ask specific questions about fulfilling their obligations.
-
A producer can grant access to anyone they would like to authorize in their reporting (i.e. Registry) portal. Producer reporting must be done in the producer account and batch data transfers are not accepted.
-
If a producer misreports their supply data to RPRA, they must contact the Compliance Team immediately by emailing registry@rpra.ca. Please include the following information in the email:
- The rationale for the change in the data
- Any data that supports the need for a correction (e.g., sales documents, audit)
- Any other information to support the change
While it is an offence to submit false or misleading information under the RRCEA, RPRA wants this corrected as quickly as possible to ensure a producer’s minimum management requirement is calculated using accurate supply data.
RPRA can only receive these requests from the primary contact on the company’s Registry account. Your request for an adjustment will be reviewed by a Compliance and Registry Officer.
-
No, only producers are required to pay RPRA program fees. The decision to make producers pay fees and cover the Authority’s costs was made to reflect the fact that the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 (RRCEA) is based on a producer responsibility framework. Although producers may hire service providers to help meet their obligations, the responsibility remains with the producer.
-
Under the Batteries, EEE, HSP, and Tire Regulations, a consumer is any end user of a product. A consumer includes an individual who obtains the product for the individual’s own use and a business that obtains the product for the business’s own use.
See our FAQ to understand “Who is a consumer under the Blue Box Regulation?”
-
Free riders are obligated parties that:
- Have not registered or reported to RPRA
- Have not established a collection and management system (if they are so required to), or;
- Are not operating a collection and management system (if they are so required to).
See our FAQs to understand “What is RPRA’s approach to free riders?”, and “What do I do if I think a business is a free rider?”
To note:
- Some producers only have requirements to register and report. Please refer to your specific program page on our website to understand producer obligations.
- Collection and management systems may be accomplished by a producer responsibility organization (PRO) on behalf of a producer through contractual arrangements between the producer and PRO. If a PRO is managing a producer’s collection and management requirements, producers must identify that PRO to RPRA.
-
RPRA takes a risk-based and proportional approach to compliance. This approach focuses on the potential risks that arise from non-compliance and assessing those risks to guide the use of compliance tools and the deployment of resources to minimize risk and maximize compliance. Learn more about RPRA’s Risk-Based Compliance Framework.
As a provincial regulator, we have the following powers to bring non-compliant parties into compliance:
- Broad inquiry powers including authority to compel documents and data
- Inspections and investigations
- Audits
- Compliance Orders and Administrative Penalty Orders (amounts to be set in regulation once finalized)
- Prosecution
RPRA’s primary approach to compliance is through communications (C4C – Communicating for Compliance). RPRA communicates directly with obligated parties and informs them of their requirements and when and how they must be completed. A high degree of compliance is achieved with this approach.
RPRA considers free riders a high priority to the programs we administer and focuses compliance efforts on bringing free riders into compliance with the regulations.
See our FAQ to understand “What is a free rider?”, and “What do I do if I think a business is a free rider?”
-
We encourage anybody who believes an entity is a free rider to contact RPRA’s Compliance and Registry Team at 1-833-600-0530 or by emailing registry@rpra.ca with information about that entity. RPRA reviews every free rider allegation that is referred to us.
We do not share information about our inspections or progress on specific free rider cases.
See our FAQ to understand “What is a free rider?” and “What is RPRA’s approach to free riders?”
-
In the Manage PRO section in the Registry, the “Service End Date” is not a mandatory field. You can leave this field blank if there is no end date in your contract. If you decide to change PROs in the future, you can update this field to the date your agreement ended with that PRO.
-
If you select credit card as your method of payment, this method of payment is done through your Registry account.
Follow these steps to complete your payment:
- When you are in the payment method section in the Registry, select credit card as your preferred method.
- Input your credit card details.
- Click submit and payment will process automatically.
Please note:
- Registry invoices are considered due on receipt.
- Invoices are in CAD funds and payments must be sent in CAD.
- Once your transaction has been approved, your payment will be reflected in your Registry account immediately.
If you have questions relating to fee payment, contact our Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or call 647-496-0530 or toll-free at 1-833-600-0530.
-
If you select bank withdrawal as your method of payment, this authorizes the Resource Productivity and Recovery Authority to make a one-time withdrawal for the Registry invoice payment from the account you provided.
Bank Withdrawal – Important Terms:
- You have authorized RPRA to make one-time debits from your account. RPRA will obtain your authorization before any additional one-time or sporadic withdrawal is debited from your account. You have agreed that this confirmation may be provided at least three (3) calendar days before the first payment is withdrawn from your account. You have waived any and all requirements for pre-notification of the account being debited.
- Your payments are being made on behalf of a business.
- Your agreement may be cancelled provided notice is received thirty (30) days before the next withdrawal. If any of the above details are incorrect, please contact us immediately at the contact information below. If the details are correct, you do not need to do anything further and your Pre-Authorized Debits (PAD) will be processed. You have certain recourse rights if any debit does not comply with these terms. For example, you have the right to receive a reimbursement for any PAD that is not authorized or is not consistent with this PAD Agreement. To obtain more information on your recourse rights, contact your financial institution or visit www.payments.ca.
Please note:
- Registry invoices are considered due on receipt.
- Invoices are in CAD funds and payments must be sent in CAD.
- It may take 1-2 weeks for the involved banks to process your payment.
If you have questions relating to fee payment, contact our Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or call 647-496-0530 or toll-free at 1-833-600-0530.
-
If you select electronic bill payment as your method of payment, this method of payment is done through your online banking account, using the bill payment functionality. It is available at major Canadian banks (e.g., TD, RBC, BMO, Scotiabank, etc.).
Follow these steps to complete your payment:
- Log in to your bank account.
- Go to the bill payment section and choose to add a payee.
- Search for and select “RPRA” as the payee.
- Once “RPRA” is selected, enter your registration number as the account number to make your payment. Your registration number can be found on your invoice.
Please note:
- Registry invoices are considered due on receipt.
- Invoices are in CAD funds and payments must be sent in CAD.
- It may take 1-2 weeks for your payment to be reflected in your Registry account once you have completed it.
If you have questions relating to fee payment, contact our Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or call 647-496-0530 or toll-free at 1-833-600-0530.
-
If you select cheque as your method of payment, follow these steps to complete your payment:
- Make your cheque payable to “Resource Productivity and Recovery Authority”
- Enter your Invoice Number on the memo line of the cheque
- Please send your cheque to*:
-
- Resource Productivity Recovery Authority
- PO Box 46114, STN A
- Toronto, ON
- M5W 4K9
*As of January 20, 2023, the address for mailing cheques to RPRA has been revised. Please update your records and send cheques to the above address going forward.
Please note:
- Registry invoices are considered due on receipt.
- Invoices are in CAD funds and payments must be sent in CAD.
- It may take 2-4 weeks for your payment to be reflected in your Registry account once you have mailed your cheque due to mail and cheque processing times.
If you have questions relating to fee payment, contact our Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or call 647-496-0530 or toll-free at 1-833-600-0530.
-
If you select electronic data interchange (EDI) as your method of payment, this is an electronic payment through your bank, also commonly known as EFT or ACH.
Follow these steps to complete your payment:
- Submit your payment using RPRA’s banking information provided on your invoice.
- Be sure to reference your Invoice Number when you submit this payment to your bank so that we will be able to identify your payment.
Please note:
- Registry invoices are considered due on receipt.
- Invoices are in CAD funds and payments must be sent in CAD.
- It may take 1-2 weeks for your payment to be reflected in your Registry account once you have completed it.
If you have questions relating to fee payment, contact our Compliance and Registry Team at registry@rpra.ca or call 647-496-0530 or toll-free at 1-833-600-0530.
-
A brand is any mark, word, name, symbol, design, device or graphical element, or a combination thereof, including a registered or unregistered trademark, which identifies a product and distinguishes it from other products.
A brand holder is a person who owns or licenses a brand or otherwise has rights to market a product under the brand.
Note:
- If there are two or more brand holders, the producer most directly connected to the production of the material is the brand holder.
- If more than one material produced by different brand holders are marketed as a single package, the producer who is more directly connected to the primary product in the package is the brand holder.
-
Account admins have access to all information within a registrant’s account. They can create and assign primary and secondary users’ access to the account, edit and submit reports, and pay fees. They are the only ones who can manage PROs. Account admins can view all activities users undertake. They will also be the recipient of emails from the Registry portal.
Primary users can only assign secondary users’ access to the account, edit and submit reports and pay fees.
Secondary users can only edit and submit reports and pay fees.
-
Starting January 1, 2023, RPRA will collect 13% HST on all fees at the time of fee payment.
This decision is based on a ruling RPRA received from the CRA in which HST must be charged on its fees under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 (RRCEA). RPRA has determined that this ruling applies to all RRCEA producer responsibility programs and the Excess Soil and Hazardous Waste programs.
On December 22, 2022, RPRA will reissue invoices that were issued prior to January 1, 2023, amended to indicate that 13% HST was paid. From December 22 onwards, registrants will be able to access the amended invoices in their Registry accounts under a new tab labelled “Invoices”. The amended invoice will show an HST amount as well as the date the amended invoice was reissued.
Important notes:
- On the amended invoices there have been no changes to the Invoice Total and registrants will not be required to pay any additional monies to RPRA for past invoices.
- Registrants may be able to claim input tax credits for the HST collected on RPRA fees, for both the amended invoices and new invoices issued January 1, 2023, onwards. However, RPRA is not in a position to provide tax advice and suggests you consult your internal or external accountants to seek their counsel.
- All new invoices issued effective January 1, 2023, will contain appropriate information identifying the amount of the HST and other relevant details. These invoices will also be displayed under the “Invoices” tab in a registrants’ Registry account.
-
Registrants can access past invoices in their Registry account under a new tab labelled “Invoices”. A banner will be displayed that highlights whether an invoice has been amended to include HST as well as the date the amended invoice was reissued. This will show on all invoices with an invoice date before December 21, 2022. See sample screenshot below.

-
Registrants can access past invoices in their Registry account under a new tab labelled “Invoices”. See sample screenshot below.
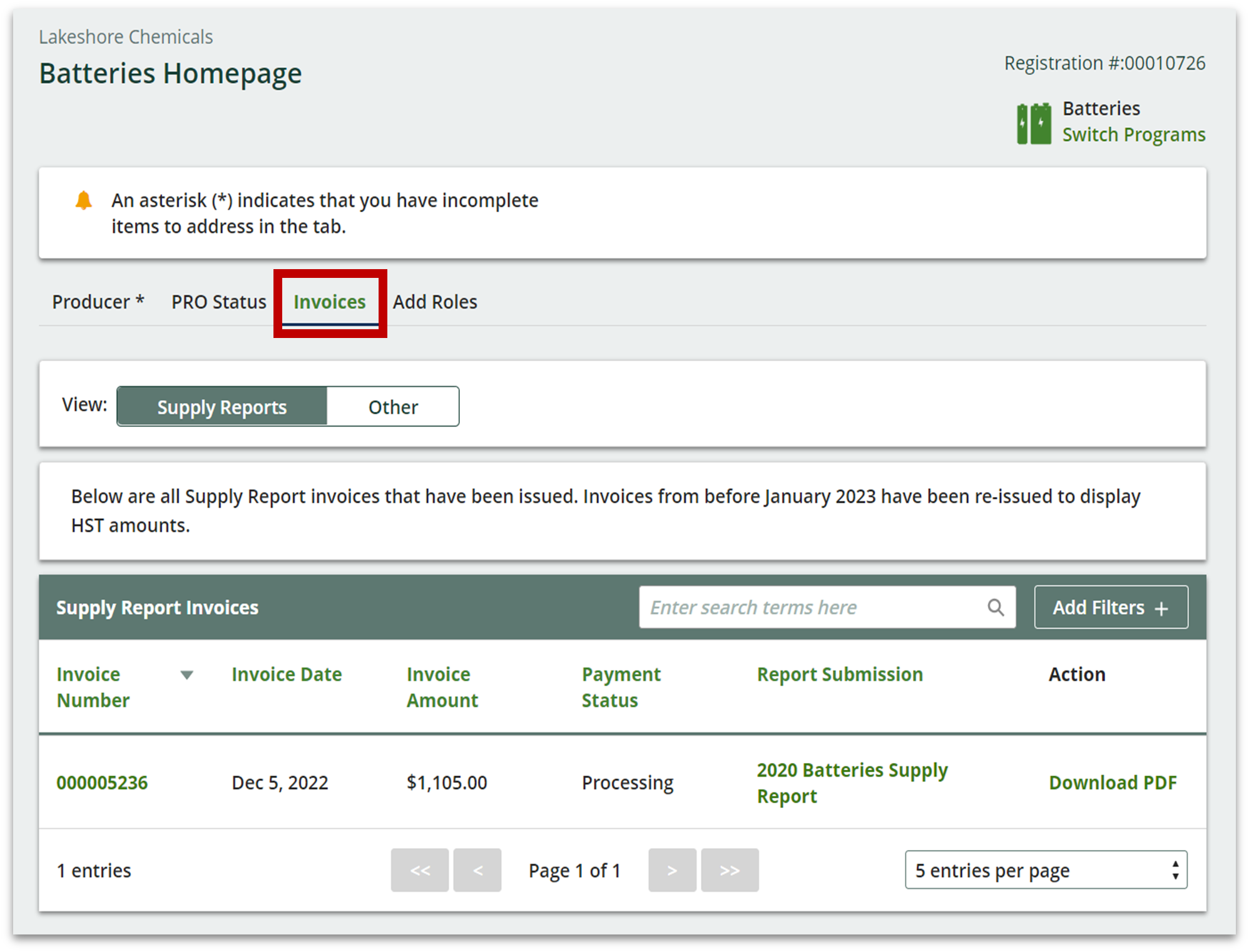
-
Failure of an obligated party to meet a registration or reporting deadline may result in compliance action, including compliance orders, prosecutions or monetary penalties issued in accordance with the Administrative Penalties Guidelines.
In accordance with the Risk Based Compliance Framework, RPRA will communicate to obligated parties, via email, about their reporting requirements in advance of submission deadlines. RPRA will also send deadline reminders and notify missed deadlines to obligated parties prior to taking further compliance action.
For more guidance, read the new Late Registration or Report Submissions Compliance Bulletin.
-
No. Effective February 6, 2023, RPRA will no longer accept requests for extensions to registration or reporting deadlines. Obligated parties should make every effort to ensure they meet all submission deadlines as part of their obligations under their associated regulation.
For more guidance, read the Late Registration or Report Submissions Compliance Bulletin.
-
Yes, a producer, a PRO (producer responsibility organization) on behalf of a producer, or a service provider on behalf of either party, can collect any product or material (including materials or products that are not designated under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 (RRCEA)). For example, a battery producer may choose to collect batteries that weigh over 5kg; a tire producer may choose to collect bicycle tires; or a Blue Box producer may choose to collect books.
Products or materials that are not designated under RRCEA regulations cannot be counted towards meeting a producer’s collection or management requirements under RRCEA.
If designated materials are co-collected with materials that are not designated, a person must use a methodology or process acceptable to the Authority to account for those materials. Anyone considering this can contact the Compliance Team to discuss at registry@rpra.ca or 833-600-0530.
For example, if bicycle tires are collected at the same time as automotive tires, they must be accounted for separately both when collected and when sent to a processor.
-
Producers are obligated parties under the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act and are ultimately responsible for their data submitted through RPRA’s Registry. Producers can choose to contract with an external consultant to support their data submission, but third parties have limited permissions in the Registry as they are not regulated parties.
A producer can choose to assign a primary or secondary user profile in their Registry account to an external consultant. An external consultant may submit supply data reports and/or pay registry fees on the producer’s behalf.
External consultants cannot submit and/or sign registration, executive attestations, account admin changes or supply data adjustment documentation on behalf of a producer. External consultants cannot be account admins, nor can they manage a PRO within the Registry on behalf of a producer.
-
Producers are not required to collect and manage their own branded products and materials. Instead, a producer is expected to collect and manage a portion of similar materials in Ontario. The portion of material that a producer collects and manages is known as their minimum management requirement. A minimum management requirement, which is set based on calculations outlined in the applicable Regulation, is the weight of the products or packaging that the producer must ensure is collected and managed. The calculated amount is proportionate to the weight of materials that producer supplied into the province.
For example, a producer who supplied laptops into Ontario does not need to collect and manage their own branded laptops. Instead, they must ensure that they collect and manage an equivalent weight of information technology, telecommunications, and audio-visual equipment (ITT/AV) materials.
Similarly, a producer who supplied cardboard boxes into Ontario does not need to collect and manage those exact cardboard boxes. Rather, they need to ensure that an equivalent weight of paper is collected and managed.
Almost all producers will work with producer responsibility organizations (PROs) for the purposes of meeting their obligations to collect and manage materials. PROs establish collection and management systems across Ontario for different material types. A producer can meet their obligations to collect and manage materials by entering into a contract with a PRO to provide these services on their behalf.
-
Account admins can manage password resets for all active users in the account. Primary users are also able to manage password resets, but only for active users within the programs they are the primary user for. If secondary users require a password reset, they can reach out to the account admin or primary user to do so.
-
The account admin or primary user navigates to the program homepage of which the user requiring a password reset is enrolled in. The account admin or primary user then clicks their username at the top right of the page to show the drop-down list and selects Manage Users.
In the Active Users table, the account admin or primary user clicks Reset Password on the row for the user they want to reset the password for and clicks Confirm.
The user’s password has now been reset. They will receive an email with a password reset link.
Note: the password reset link will expire within 24 hours. If the link expires before the user creates a new password, the account admin or primary must click “Reset Password” again to restart the process.
See the FAQ: Who can reset passwords in the registry?
-
If you need to change an email address in your registry account, please contact the Compliance Team at registry@rpra.ca. Registry users cannot update email addresses themselves; this can only be completed by RPRA.
-
No. Recycling drop-off locations displayed on the map cannot:
- charge the public a fee to drop off materials that the location accepts.
- refuse the drop-off of materials displayed on the map. However, recycling locations can request reasonable requirements when consumers drop off an item to ensure health and safety. For example, sites may require that used oil filters are dropped off in sealed containers, light tubes are taped together, etc.
If you are charged a fee or refused drop off, you can report an issue about that specific location to RPRA (see our other FAQ for further instructions).
-
If the map is not showing any recycling locations near you, you can:
- Try expanding your search by increasing the distance you’re willing to travel or modifying other filters.
- If there still isn’t a recycling location near you, contact the waste management department at your municipality for proper disposal instructions.
-
If you experience an issue when dropping off your recyclables at a location displayed on the map, click the ‘Report an Issue’ link on that specific location. This link will open a form for you to fill out about the issue. RPRA’s Compliance Team will review the issue reported and take action, as necessary.
You may report an issue to RPRA because the recycling location: - Charges you a fee to drop off materials accepted for recycling.
- *Refuses to accept your materials for recycling (only applicable if your materials are in line with the examples provided on the map).
- Displayed on the map does not actually exist.
- Is not open to the public or does not accept the materials during its business hours.
*Note: Recycling locations can request reasonable requirements when consumers drop off an item to ensure health and safety. For example, sites may require that used oil filters are dropped off in sealed containers, light tubes are taped together, etc.
-
Typically, only municipal depots may require valid IDs when dropping off materials to recycle to confirm you live in that municipality. It is recommended to bring your ID with you to any location, just in case.
-
The recycling locations that appear on the map are reported to RPRA by businesses that run the recycling systems in Ontario.
-
The recycling locations that appear on the map are reported to RPRA by PROs (or producers managing their own collection networks) as the administrators of the collection systems. The public collection activities that PROs report in their registry account are uploaded to the map in near real-time.
-
Registrants may request that a Deputy Registrar review a Compliance Order issued to them by an inspector. The request must be made, in writing, by the registrant to a Deputy Registrar within seven days of being served with the order. The request must include:
- The parts of the order that the request for review pertains to;
- Any submissions the person requesting the review wants considered; and
- An address (physical or electronic) where the person can be served with the Deputy Registrar’s decision.
A Deputy Registrar will then review the order and can revoke, confirm, or amend the inspector’s order.
Deputy Registrars must either issue their decision or provide notice that more time is needed within seven days of receiving the request. If a Deputy Registrar provides notice that more time is needed, they must stay (put on hold) the order while it is under review, and the Deputy Registrar must issue their decision within 90 days.
If a Deputy Registrar does not issue a decision or provide notice that more time is needed within seven days of receiving the request for review, the order will remain as originally issued.
Note: This FAQ is for general information only and should not be considered legal advice. Please review the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 and associated regulations for details.
See the FAQ: ‘Can I appeal a Compliance Order issued to me?’ for information on appealing a compliance order.
-
Registrants who receive a Notice of Intention to issue an Administrative Penalty Order may request that the Registrar or a Deputy Registrar consider additional information before they decide to issue the order. A registrant may ask the Registrar or a Deputy Registrar to review:
- Additional information related to the contravention;
- Any information relevant to the determination of the penalty amount; or
- Any actions you have taken to remedy the contravention since it occurred.
The request must be made to the Registrar or a Deputy Registrar, in writing, within 21 days of the notice of intention being served on the registrant. All additional information and supporting documentation that the registrant would like the Registrar or Deputy Registrar to consider should be included in the request.
The Registrar or Deputy Registrar must then consider the information in the request and determine whether or not to issue an order. If the Registrar or Deputy Registrar decides not to issue the order, they must notify the registrant of this decision.
See RPRA’s Administrative Penalties Guideline for further information or the FAQ: ‘Can I appeal an Administrative Penalty Order issued to me?’ for information on appealing an administrative penalty order.
Note: This FAQ is for general information only and should not be considered legal advice. Please review the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 and associated regulations for details.
-
Registrants may appeal an Administrative Penalty Order issued to them to the Ontario Land Tribunal (OLT). The registrant must serve written notice of their intention to appeal to the OLT and to the Registrar or a Deputy Registrar within 15 days of being served the order. The order will be temporarily stayed (put on hold) until a decision is rendered by the tribunal. The notice must include:
- The parts of the order that the appeal pertains to; and
- The grounds on which the person appealing the order intends to rely at the hearing.
The OLT will hold a hearing, and the OLT may confirm, vary, or revoke the order. The OLT cannot vary the amount of the penalty unless it considers the amount to be unreasonable.
After a matter is decided by the OLT, the registrant or RPRA may appeal the OLT’s decision to the Divisional Court, but only on a question of law and with leave (permission) of the Divisional Court. If a party obtains leave, the appeal of the OLT decision will be heard by the Divisional Court. This process is governed by the Rules of Civil Procedure. The OLT’s decision is not automatically stayed by an appeal to the Divisional Court, but a stay may be granted by the OLT or the Court.
See RPRA’s Administrative Penalties Guideline for further information.
Note: This FAQ is for general information only and should not be considered legal advice. Please review the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 and associated regulations for details.
-
If a Compliance Order is issued to a registrant by the Registrar or a Deputy Registrar, or if the registrant receives a decision from a Deputy Registrar issued as a result of a Request for Review of an inspector’s order, the registrant can appeal the order to the Ontario Land Tribunal (OLT). The registrant must serve written notice of their intention to appeal to the Registrar or Deputy Registrar who made the order and to the OLT within 15 days of being served with the order. The notice must include:
- The parts of the order that the appeal pertains to; and
- The grounds on which the person appealing the order intends to rely at the hearing.
The OLT will hold a hearing. The OLT may decide to confirm, vary, or revoke the order.
After a matter is decided by the OLT, the registrant or RPRA may appeal the OLT’s decision to the Divisional Court, but only on a question of law and with leave (permission) of the Divisional Court. If a party obtains leave, the appeal of the OLT decision will be heard by the Divisional Court. This process is governed by the Rules of Civil Procedure. The OLT’s decision is not automatically stayed (put on hold) by an appeal to the Divisional Court, but a stay may be granted by the OLT or the Court.
Note: This FAQ is for general information only and should not be considered legal advice. Please review the Resource Recovery and Circular Economy Act, 2016 and associated regulations for details.
-
A collection site is required to:
- accept all used materials that are designated under the program the collection site operates under*,
- accept materials dropped off free of charge, and
- accept materials dropped off during regular business hours.
The amount and type of materials a collection site must accept varies by which recycling program they operate under.
*More information on what materials must be accepted for each recycling program can be found here.
-
Collection site names are taken from Google Maps. If the name is wrong, request to change it through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by providing the correct name.
-
Only your PRO can update collection site addresses. Ask your PRO to remove the old address from their collection network and add the new address.
The Compliance Team is unable to make changes to the address of a site that has been reported.
-
Business hours are taken from Google Maps. If the information on Google Maps is incorrect, update your Google account information by following these steps. Note: there may be a delay between the time you update your information in Google and it showing on RPRA’s map.
If the information on Google Maps is correct and not showing on the Where to Recycle map, request to change it through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by providing the correct business hours.

-
Phone numbers are taken from Google Maps. If the information on Google Maps is incorrect, update your Google account information by following these steps. Note: there may be a delay between the time you update your information in Google and it showing on RPRA’s map.
If the information on Google Maps is correct and not showing on the Where to Recycle map, request to change it through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by providing the correct phone number.

-
Websites are taken from Google Maps. If the information on Google Maps is incorrect, update your Google account information by following these steps. Note: there may be a delay between the time you update your information in Google and it showing on RPRA’s map.
If the information on Google Maps is correct and not showing on the Where to Recycle map, request to change it through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by providing the correct website link.

-
Wrong materials showing
If your site doesn’t collect the material(s) listed on the map, you can submit a request to change it through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by providing which materials should be removed.
Materials not showing
If you collect more materials than what is listed on the map, contact your PRO and they’ll update your collection site information.
If you aren’t already working with a PRO for a specific material and want to add a material to your collection site, you can find a list of PROs and contact information on the applicable program page of RPRA’s website.
-
First, contact your PRO to confirm if the collection site should be considered private or if it can be removed entirely from their collection system. If they confirm it can be removed from the system, ask them to deactivate it so it no longer appears on the map.
If you aren’t working with a PRO, request to remove your collection site through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form asking to remove the collection site.

-
A public collection site must be readily accessible to the public and accept designated used materials during regular business hours. Publicly accessible collection sites and events appear on the Where to Recycle map.
A private collection site (e.g. office or school that collects designated materials) does not need to be publicly accessible. Private collection sites do not appear on the map.
Read this related FAQ: What does it mean for a collection site to be readily accessible to the public?
-
If your collection site isn’t part of a PRO’s collection network, it won’t appear on the map. The map populates collection sites with data entered by producers or PROs on their behalf.
If you are working with a PRO and your site is not listed on the map, contact your PRO.
If you aren’t already working with a PRO and want to add your collection site to the map, you can find a list of PROs and their contact information on the applicable program page of RPRA’s website.
-
Municipalities are required to accept materials from the sectors identified in their Environmental Compliance Approval (ECA). Municipalities are not required to accept more than what their ECA requires them to.
-
To delete a duplicate collection site, submit a request through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by asking to remove the duplicate collection site.

If the request is for multiple locations, contact the Compliance Team at registry@rpra.ca with the following information:
- the issue,
- name and address for each collection site, and
- your contact information.
-
To update the type of collection site, submit a request through the map directly by:
- looking up the location,
- clicking the location,
- clicking the ‘Report an issue for this location’ link, and
- filling out the form by providing the correct collection site type.

If the request is for multiple locations, contact the Compliance Team at registry@rpra.ca with the following information:
- the issue,
- name and address for each collection site, and
- your contact information.
-
Readily accessible to the public means a site can be accessed by any consumer who wants to drop off used materials for free to be recycled, reused or refurbished.
A public collection site cannot restrict the type of products accepted. For example, an electronics collection site cannot refuse to accept printers or large televisions. Retail stores are only required to accept materials of a similar size and function to the products supplied at that location. For example, a mobile phone kiosk may choose to accept only mobile phones.
Collection sites can request reasonable requirements when consumers drop off an item to ensure health and safety. For example, sites may require that used oil filters are dropped off in sealed containers, light tubes are taped together, etc.
Publicly accessible collection sites and events will appear on the Where to Recycle map.
Restrictions
If a collection site has restrictions, for example due to an Environmental Compliance Approval (ECA), municipal by-law, or fire code provision, the restrictions may be applied, and the collection site will still be considered readily accessible to the public. For example, a municipal depot that has an ECA to accept materials only from residents of the community can apply this restriction and still be considered readily accessible to the public. Similarly, a collection site with an ECA that prohibits collection from the industrial, commercial and institutional sectors may apply these restrictions and still be considered readily accessible to the public. And a collection site that has restrictions on how it can be accessed (such as drive-in only) may enforce these restrictions and still be considered readily accessible to the public.
Read this related FAQ: What is the difference between a public and private collection site?
-
If a producer or service provider needs to adjust the performance data reported to RPRA, they must contact the Compliance Team immediately by emailing registry@rpra.ca. Please include the following information in the email:
- The rationale for the change in the data
- Any data that supports the need for a correction (e.g., tonnage purchase or sale contract, audit)
- Any other information to support the change
While it is an offence to submit false or misleading information under the RRCEA, RPRA wants this corrected as quickly as possible to ensure that it has accurate performance data from all registrants.
RPRA can only receive these requests from the primary contact on the company’s Registry account. Your request for an adjustment will be reviewed by a Compliance and Registry Officer.